
|
|
PDF CR16MBR5 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | CR16MBR5 | |
| Descripción | Family of 16-bit CAN-enabled CompactRISC Microcontrollers | |
| Fabricantes | National Semiconductor | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de CR16MBR5 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 70 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
January 2002
CR16HCS5/CR16HCS9/CR16MAR5/CR16MAS5
CR16MAS9/CR16MBR5/CR16MCS5/CR16MCS9
Family of 16-bit CAN-enabled CompactRISC
Microcontrollers
1.0 General Description
The family of 16-bit CompactRISC™ microcontroller is
based on a Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) ar-
chitecture. The device operates as a complete microcom-
puter with all system timing, interrupt logic, flash program
memory or ROM memory, RAM, EEPROM data memory,
and I/O ports included on-chip. It is ideally suited to a wide
range of embedded controller applications because of its
high performance, on-chip integrated features and low
power consumption resulting in decreased system cost.
The device offers the high performance of a RISC architec-
ture while retaining the advantages of a traditional Com-
plex Instruction Set Computer (CISC): compact code, on-
chip memory and I/O, and reduced cost. The CPU uses a
three-stage instruction pipeline that allows execution of up
to one instruction per clock cycle, or up to 25 million in-
structions per second (MIPS) at a clock rate of 24 MHz.
The device contains a FullCAN class, CAN serial interface
for low/high speed applications with 15 orthogonal mes-
sage buffers, each supporting standard as well as extend-
ed message identifiers.
Block Diagram
CR16B
RISC Core
Processing
Unit
Core Bus
Fast Clk Slow Clk*
Clock Generator
Power-on-Reset
CR16CAN
FullCAN 2.0B
Peripheral
Bus
Controller
64k-Byte
Flash
Program
Memory
3k-Byte
RAM
2176-Byte
EEPROM
Data
Memory
1.5k-Byte
ISP
Memory
Interrupt
Control
Power
Manage-
ment
Timing and
Watchdog
Peripheral Bus
I/O
µWire/SPI
2x
USART
ACCESS
bus
4x
VTU
2x 12-ch
MFT 8-bit A/D
MIWU
2 Analog
Comparators
Please note that not all family members contain same peripheral modules and features.
TRI-STATE® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
©2001 National Semiconductor Corporation
www.national.com
1 page 
3.0 Device Overview
The devices are complete microcomputers with all system
timing, interrupt logic, program memory, data memory, and I/
O ports included on-chip, making it well-suited to a wide
range of embedded controller applications.
3.1 CR16B CPU CORE
The device uses a CR16B CPU core module. This is the
same core used in other CompactRISC family member de-
signs, like DECT or GSM chipsets.
The high performance of the CPU core results from the im-
plementation of a pipelined architecture with a two-bytes-per-
cycle pipelined system bus. As a result, the CPU can support
a peak execution rate of one instruction per clock cycle.
Compared with conventional RISC processors, the device
differs in the following ways:
— The CPU core can use on-chip rather than external
memory. This eliminates the need for large and com-
plex bus interface units.
— Most instructions are 16 bits, so all basic instructions
are just two bytes long. Additional bytes are sometimes
required for immediate values, so instructions can be
two or four bytes long.
— Non-aligned word access is allowed. Each instruction
can operate on 8-bit or 16-bit data.
— The device is designed to operate with a clock rate in
the 10 to 24 MHz range rather than 100 MHz or more.
Most embedded systems face EMI and noise con-
straints that limit clock speed to these lower ranges. A
lower clock speed means a simpler, less costly silicon
implementation.
— The instruction pipeline uses three stages. A smaller
pipeline eliminates the need for costly branch predic-
tion mechanisms and bypass registers, while maintain-
ing adequate performance for typical embedded
controller applications.
For more information, please refer to the CR16B Program-
mer’s Reference Manual, Literature #: 633150.
3.2 MEMORY
The CompactRISC architecture supports a uniform linear ad-
dress space of 2 megabytes. The device implementation of
this architecture uses only the lowest 128K bytes of address
space. Four types of on-chip memory occupy specific inter-
vals within this address space:
• 64K bytes of flash EEPROM program memory (100K cy-
cles)
• 48K bytes ROM programm memory version available also
(100K cycles)
• 3K bytes of static RAM
• 2K bytes of EEPROM data memory with low endurance
(25K cycles)
• 128 bytes with high endurance (100K cycles)
• 1.5K bytes flash EEPROM memory for ISP code
The 3K bytes of static RAM are used for temporary storage
of data and for the program stack and interrupt stack. Read
and write operations can be byte-wide or word-wide, depend-
ing on the instruction executed by the CPU. Each memory
access requires one clock cycle; no wait cycles or hold cycles
are required.
There are two types of flash EEPROM data memory storage.
The 2K bytes of EEPROM data memory with low endurance
(25K cycles) and 128 bytes of flash EEPROM data memory
with high endurance (100K cycles) are used for non-volatile
storage of data, such as configuration settings entered by the
end-user.
The 64K bytes of flash EEPROM program memory are used
to store the application program. It has security features to
prevent unintentional programming and to prevent unautho-
rized access to the program code. This memory can be pro-
grammed with a device external programming unit or with the
device installed in the application system (in-system pro-
gramming).
There is a factory programmed boot memory used to store
In-System-Programming (ISP) code. (This code allows pro-
gramming of the program memory via one of the USART in-
terfaces in the final application.)
For flash EEPROM program and data memory, the device in-
ternally generates the necessary voltages for programming.
No additional power supply is required.
3.3 INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS
The device has 56 software-configurable I/O pins, organized
into seven 8-pin ports called Port B, Port C, Port F, Port G,
Port H, Port I, and Port L. Each pin can be configured to op-
erate as a general-purpose input or general-purpose output.
In addition, many I/O pins can be configured to operate as a
designated input or output for an on-chip peripheral module
such as the USART, timer, A/D converter, or MICROWIRE/
SPI interface.
The I/O pin characteristics are fully programmable. Each pin
can be configured to operate as a TRI-STATE output, push-
pull output, weak pull-up input, or high-impedance input.
3.4 BUS INTERFACE UNIT
The Bus Interface Unit (BIU) controls the interface between
the on-chip modules to the internal core bus. It determines
the configured parameters for bus access (such as the num-
ber of wait states for memory access) and issues the appro-
priate bus signals for each requested access.
The BIU uses a set of control registers to determine how
many wait states and hold states are to be used when ac-
cessing flash EEPROM program memory, ISP memory and
the I/O area (Port B and Port C). Upon start-up the configu-
ration registers are set for slowest possible memory access.
To achieve fastest possible program execution, appropriate
values should be programmed. These settings vary with the
clock frequency and the type of on-chip device being access-
ed.
5 www.national.com
5 Page 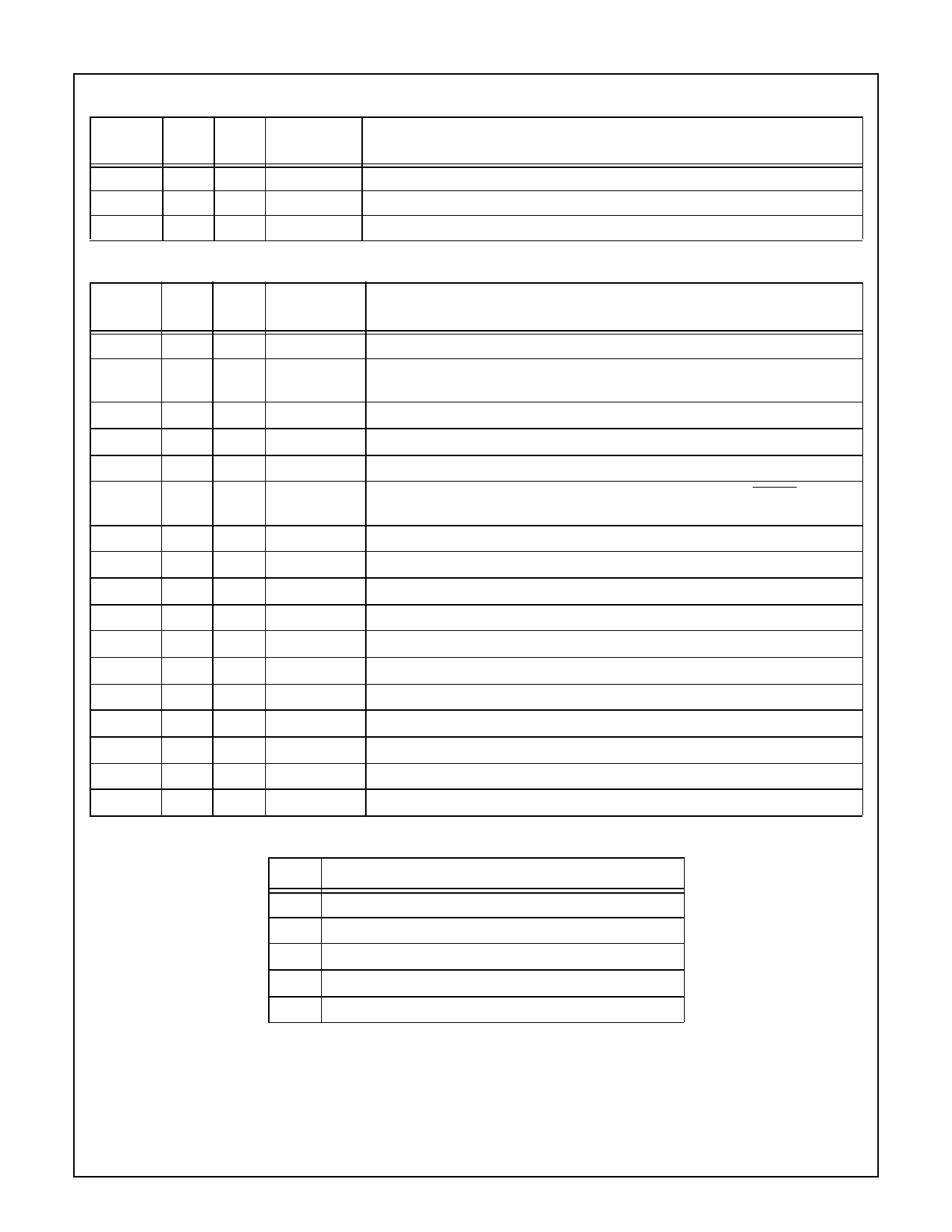
Table 3 Output Pins
Signal
Type
Active
Pin (* for
a shared pin)
Function
TDX1
CMOS High *
USART 1 transmit data output (shared with PG6).
TDX2
CANTx
CMOS High *
CMOS High
USART 2 transmit data output (shared with PG1).
CAN output.
Table 4 Input/Output Pins
Pin (* for a
Signal Type Active shared pin)
Function
PF[0:7]
PG[0:7]
CMOS High
CMOS High
*
*
PB[0:7]
PC[0:7]
CMOS High
CMOS High
*
*
Generic I/O port. Shared with T1A, T1B, TIO1, TIO2, T2A, T2B, TIO3, TIO4.
Generic I/O port. Shared with RDX2, TDX2, CKX2, TIO5, TIO6, RDX1, TDX1,
CKX1.
Generic I/O port.
Generic I/O port.
PL[0:7]
PH[0:7]
CMOS High
CMOS High
*
*
Generic I/O port. Shared with 6 comparator pins, MIWU16 on PL0:3.
Generic I/O port. Shared with ADC input channels 8-11, MWCS, MDIDO,
MDODI, MSK; MIWU16 on PH4:7.
PI[0:7]
T1A
CMOS High
CMOS Prog
*
*
Generic I/O port. Shared with ADC input channels 0-7.
Timer 1 input A. Shared with I/O port pin PF0.
T2A
TIO[0:7]
MDIDO
MDODI
MSK
CKX1
CKX2
CMOS Prog
CMOS Prog
CMOS High
CMOS High
CMOS Prog
CMOS High
CMOS High
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Timer 2 input A. Shared with I/O port pin PF4.
Versatile timer unit I/Os. Shared with PF2:3, PF6:7, PG3:4, PL6:7.
Master In/Slave Out port: SPI/Microwire. Shared with I/O pin PH5,
Master Out/Slave In port: SPI/Microwire. Shared with I/O pin PH6.
SPI/Microwire clock. Shared with I/O pin PH7.
USART 1 clock. Shared with I/O pin PG7.
USART 2 clock. Shared with I/O pin PG2
SCL
SDA
CMOS High
CMOS High
ACCESS.bus clock I/O.
ACCESS.bus data I/O.
Table 5 Power Supply
Signal
Function
Vcc Main digital power supply (4 total).
Vref Voltage reference supply for analog to digital converter.
AVcc Analog power supply for analog/digital converter.
AGND Analog reference ground supply.
GND Main digital reference ground (8 total).
11 www.national.com
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 70 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet CR16MBR5.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| CR16MBR5 | Family of 16-bit CAN-enabled CompactRISC Microcontrollers | National Semiconductor |
| CR16MBR5 | 16-bit CAN-enabled CompactRISC Microcontrollers (Rev. B) | Texas Instruments |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
