
|
|
PDF HC5526CP Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | HC5526CP | |
| Descripción | ITU CO/PABX SLIC with Low Power Standby | |
| Fabricantes | Intersil Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de HC5526CP (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 18 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
Data Sheet
HC5526
October 1998
File Number 4151.6
ITU CO/PABX SLIC with Low Power
Standby
The HC5526 is a subscriber line interface circuit that is
compliant with CCITT standards. Enhancements include
immunity to circuit latch-up during hot plug and absence of
false signaling in the presence of longitudinal currents.
The HC5526 is fabricated in a High Voltage Dielectrically
Isolated (DI) Bipolar Process that eliminates leakage
currents and device latch-up problems normally associated
with Junction Isolated (JI) ICs. The elimination of the
leakage currents results in improved circuit performance for
wide temperature extremes. The latch free benefit of the DI
process guarantees operation under adverse transient
conditions. This process feature makes the HC5526 ideally
suited for use in harsh outdoor environments.
Ordering Information
PART NUMBER
HC5526CM
HC5526CP
HC5526IM
HC5526IP
TEMP.
RANGE (oC)
PACKAGE
0 to 70 28 Ld PLCC
0 to 70 22 Ld PDIP
-40 to 85 28 Ld PLCC
-40 to 85 22 Ld PDIP
PKG.
NO.
N28.45
E22.4
N28.45
E22.4
Block Diagram
Features
• DI Monolithic High Voltage Process
• Programmable Current Feed (20mA to 60mA)
• Programmable Loop Current Detector Threshold and
Battery Feed Characteristics
• Ground Key and Ring Trip Detection
• Compatible with Ericsson’s PBL3764
• Thermal Shutdown
• On-Hook Transmission
• Wide Battery Voltage Range (-24V to -58V)
• Low Standby Power
• Meets CCITT Transmission Requirements
• -40oC to 85oC Ambient Temperature Range
Applications
• On-Premises (ONS)
• Key Systems
• PBX
• Related Literature
- AN9537, Operation of the HC5513/26 Evaluation Board
RINGRLY
DT
DR
TIP
RING
HPT
HPR
RING RELAY
DRIVER
RING TRIP
DETECTOR
2-WIRE
INTERFACE
VBAT
VCC
VEE
AGND
BGND
BIAS
LOOP CURRENT
DETECTOR
GROUND KEY
DETECTOR
4-WIRE
INTERFACE
VF SIGNAL
PATH
DIGITAL
MULTIPLEXER
VTX
RSN
E0
E1
C1
C2
DET
RD
RDC
RSG
57 CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207 | Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
1 page 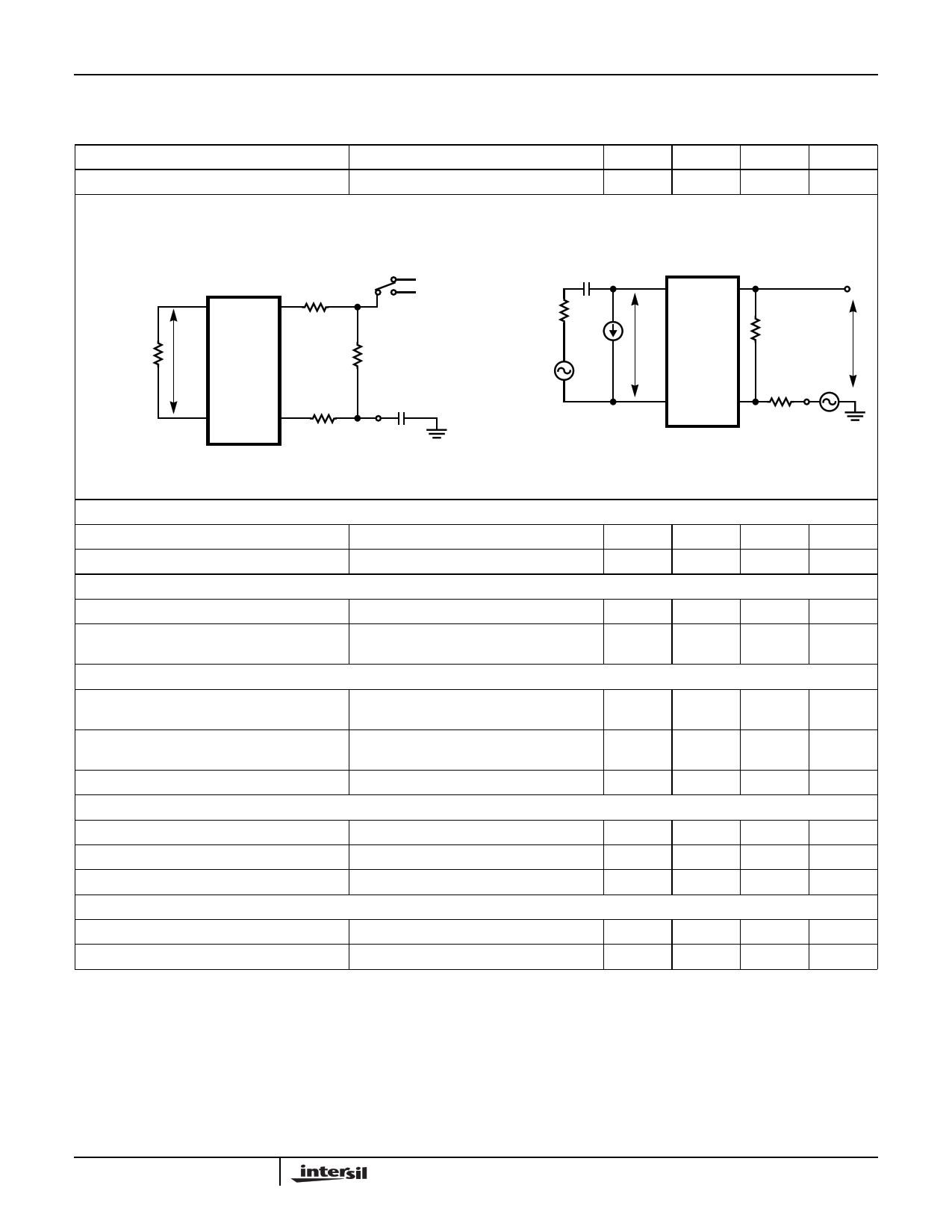
HC5526
Electrical Specifications
TA = 0oC to 70oC, VCC = 5V ±5%, VEE = -5V ±5%, VBAT = -28V, AGND = BGND = 0V, RDC1 = RDC2 = 41.2kΩ,
RD = 39kΩ, RSG = ∞, RF1 = RF2 = 0Ω, CHP = 10nF, CDC = 1.5µF, ZL = 600Ω, Unless Otherwise Specified. All
pin number references in the figures refer to the 28 lead PLCC package. (Continued)
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
4-Wire to 2-Wire
-55dBm to -40dBm (Note 22, Figure 9)
- ±0.03 -
dB
GRX = ((VTR1- VTR2)(300k))/(-3)(600)
Where: VTR1 is the Tip to Ring Voltage with VRSN = 0V
and VTR2 is the Tip to Ring Voltage with VRSN = -3V VRSN = 0V
TIP RSN
27 16
RRX
300kΩ
VRSN = -3V
RL
600Ω
VTR
RDC1
41.2kΩ
RING RDC
28 14
RDC2
41.2kΩ
CDC
1.5µF
C
RL
600Ω
IDCMET
EG
1/ωC << RL
TIP VTX
27 19
VTR
RING RSN
28 16
RT
600kΩ
VTX
RRX
ERX
300kΩ
FIGURE 8. CURRENT GAIN-RSN TO METALLIC
FIGURE 9. FREQUENCY RESPONSE, INSERTION LOSS, GAIN
TRACKING AND HARMONIC DISTORTION
NOISE
Idle Channel Noise at 2-Wire
C-Message Weighting (Note 23, Figure 10)
-
10
- dBrnC
Idle Channel Noise at 4-Wire
C-Message Weighting (Note 24, Figure 10)
-
10
- dBrnC
HARMONIC DISTORTION
2-Wire to 4-Wire
0dBm, 1kHz (Note 25, Figure 7)
- -65 -54 dB
4-Wire to 2-Wire
0dBm, 0.3kHz to 3.4kHz (Note 26,
Figure 9)
- -65 -54 dB
BATTERY FEED CHARACTERISTICS
Constant Loop Current Tolerance
RDCX = 41.2kΩ
Loop Current Tolerance (Standby)
Open Circuit Voltage (VTIP - VRING)
LOOP CURRENT DETECTOR
On-Hook to Off-Hook
Off-Hook to On-Hook
Loop Current Hysteresis
GROUND KEY DETECTOR
I0Lo=C2to50700/(oRCD(CN1o+teR2D7C) 2),
IL = (VBAT-3)/(RL +1800),
0oC to 70oC (Note 28)
0oC to 70oC, (Active)
RD = 39kΩ, 0oC to 70oC
RD = 39kΩ, 0oC to 70oC
RD = 39kΩ, 0oC to 70oC
0.9IL
IL
1.1IL
mA
0.8IL
IL
1.2IL
mA
14 - 20 V
372/RD
325/RD
25/RD
465/RD
405/RD
60/RD
558/RD
485/RD
95/RD
mA
mA
mA
Tip/Ring Current Difference - Trigger
(Note 29, Figure 11)
8 12 17 mA
Tip/Ring Current Difference - Reset
(Note 29, Figure 11)
3 7 12 mA
61
5 Page 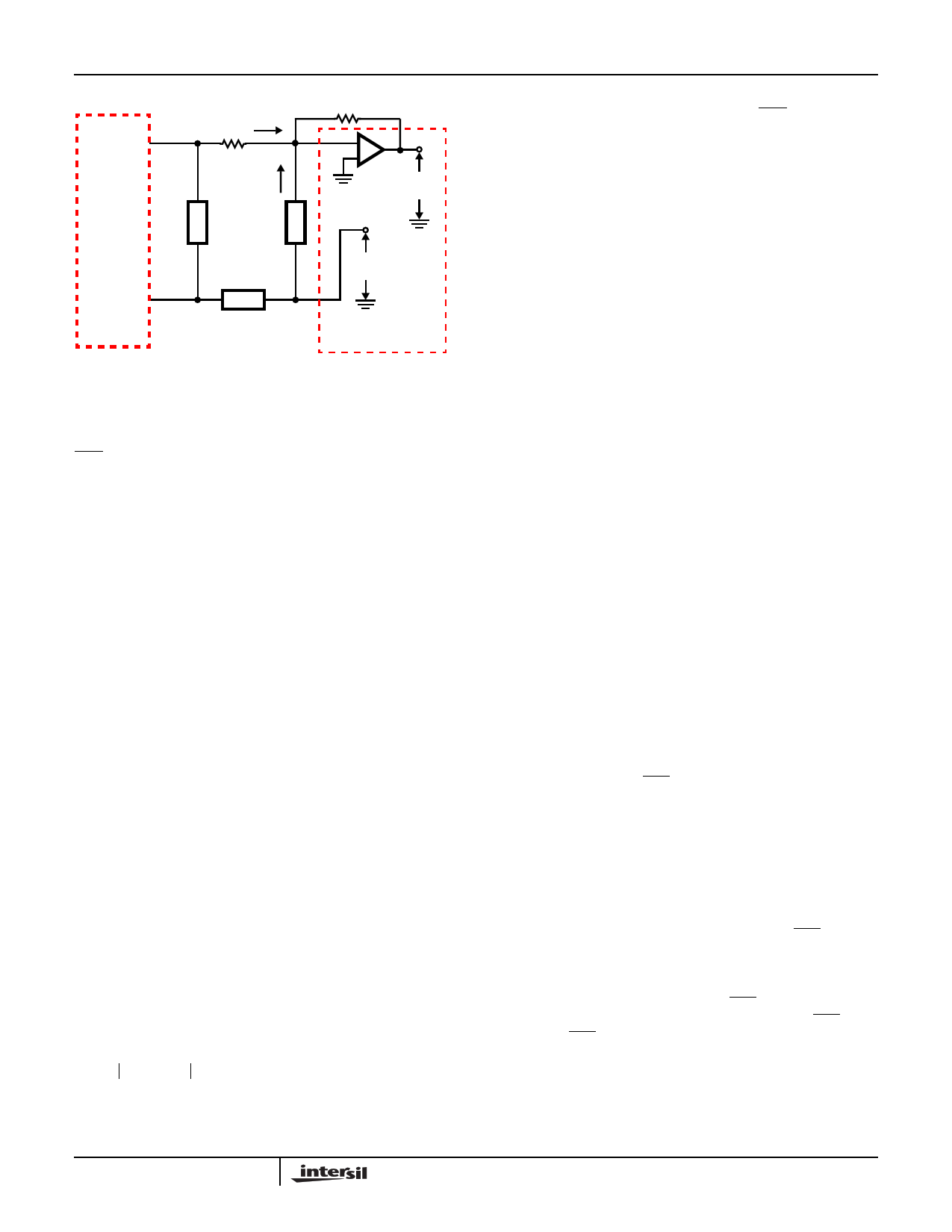
HC5526
VTX
RTX
I2
HC5526
ZT
I1
ZB
RFB
-
+
+
VTX
-
RSN
ZRX
+
VRX
-
CODEC/
FILTER
FIGURE 17. TRANSHYBRID CIRCUIT
Supervisory Functions
The loop current, ground key and the ring trip detector
outputs are multiplexed to a single logic output pin called
DET. See Table 1 to determine the active detector for a given
logic input. For further discussion of the logic circuitry see
section titled “Digital Logic Inputs”.
Before proceeding with an explanation of the loop current
detector, ground key detector and later the longitudinal
impedance, it is important to understand the difference
between a “metallic” and “longitudinal” loop currents. Figure 18
illustrates 3 different types of loop current encountered.
Case 1 illustrates the metallic loop current. The definition of
a metallic loop current is when equal currents flow out of tip
and into ring. Loop current is a metallic current.
Cases 2 and 3 illustrate the longitudinal loop current. The
definition of a longitudinal loop current is a common mode
current, that flows either out of or into tip and ring
simultaneously. Longitudinal currents in the on-hook state
result in equal currents flowing through the sense resistors
R1 and R2 (Figure 18). And longitudinal currents in the off-
hook state result in unequal currents flowing through the
sense resistors R1 and R2. Notice that for case 2,
longitudinal currents flowing away from the SLIC, the current
through R1 is the metallic loop current plus the longitudinal
current; whereas the current through R2 is the metallic loop
current minus the longitudinal current. Longitudinal currents
are generated when the phone line is influenced by
magnetic fields (e.g., power lines).
Loop Current Detector
Figure 18 shows a simplified schematic of the loop current
and ground key detectors. The loop current detector works by
sensing the metallic current flowing through resistors R1 and
R2. This results in a current (IRD) out of the transconductance
amplifier (gm1) that is equal to the product of gm1 and the
metallic loop current. IRD then flows out the RD pin and
through resistor RD to VEE. The value of IRD is equal to:
IRD
=
--I--T----I-P-----–-----I--R----I--N----G----
600
=
---I--L----
300
(EQ. 24)
The IRD current results in a voltage drop across RD that is
compared to an internal 1.25V reference voltage. When the
voltage drop across RD exceeds 1.25V, and the logic is
configured for loop current detection, the DET pin goes low.
The hysteresis resistor RH adds an additional voltage
effectively across RD, causing the on-hook to off-hook
threshold to be slightly higher than the off-hook to on-hook
threshold.
Taking into account the hysteresis voltage, the typical value
of RD for the on-hook to off-hook condition is:
RD = I--O-----N-----–----H----O-----O----K----4--t-6-o---5--O-----F---F-----–----H----O----O-----K--
(EQ. 25)
Taking into account the hysteresis voltage, the typical value
of RD for the off-hook to on-hook condition is:
RD = I--O-----F----F----–----H----O-----O----K-3---7--t--5o-----O-----N-----–----H----O----O-----K--
(EQ. 26)
A filter capacitor (CD) in parallel with RD will improve the
accuracy of the trip point in a noisy environment. The value
of this capacitor is calculated using the following Equation:
CD = R---T--D--
where: T = 0.5ms.
(EQ. 27)
Ground Key Detector
A simplified schematic of the ground key detector is shown in
Figure 18. Ground key, is the process in which the ring
terminal is shorted to ground for the purpose of signaling an
Operator or seizing a phone line (between the Central Office
and a Private Branch Exchange). The Ground Key detector is
activated when unequal current flow through resistors R1 and
R2. This results in a current (IGK) out of the transconductance
amplifier (gm2) that is equal to the product of gm2 and the
differential (ITIP -IRING) loop current. If IGK is less than the
internal current source (I1), then diode D1 is on and the output
of the ground key comparator is low. If IGK is greater than the
internal current source (I1), then diode D2 is on and the output
of the ground key comparator is high. With the output of the
ground key comparator high, and the logic configured for
ground key detect, the DET pin goes low. The ground key
detector has a built in hysteresis of typically 5mA between its
trigger and reset values.
Ring Trip Detector
Ring trip detection is accomplished with the internal ring trip
comparator and the external circuitry shown in Figure 19. The
process of ring trip is initiated when the logic input pins are in the
following states: E0 = 0, E1 = 1/0, C1 = 1 and C2 = 0. This logic
condition connects the ring trip comparator to the DET output,
and causes the Ringrly pin to energize the ring relay. The ring
relay connects the tip and ring of the phone to the external
circuitry in Figure 19. When the phone is on-hook the DT pin is
more positive than the DR pin and the DET output is high. For
off-hook conditions DR is more positive than DT and DET goes
low. When DET goes low, indicating that the phone has gone
off-hook, the SLIC is commanded by the logic inputs to go into
the active state. In the active state, tip and ring are once again
connected to the phone and normal operation ensues.
67
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 18 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet HC5526CP.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| HC5526CM | ITU CO/PABX SLIC with Low Power Standby | Intersil Corporation |
| HC5526CP | ITU CO/PABX SLIC with Low Power Standby | Intersil Corporation |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
