
|
|
PDF IS61DDB24M18 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | IS61DDB24M18 | |
| Descripción | DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO Synchronous SRAMs | |
| Fabricantes | Integrated Silicon Solution | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de IS61DDB24M18 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 25 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
72 Mb (2M x 36 & 4M x 18)
.
DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO Synchronous SRAMs
November 2009
Features
• 2M x 36 or 4M x 18.
• On-chip delay-locked loop (DLL) for wide data
valid window.
• Common data input/output bus.
• Synchronous pipeline read with self-timed late
write operation.
• Double data rate (DDR-II) interface for read and
write input ports.
• Fixed 2-bit burst for read and write operations.
• Clock stop support.
• Two input clocks (K and K) for address and con-
trol registering at rising edges only.
• Two input clocks (C and C) for data output con-
trol.
• Industrial temperature available upon request.
• Two echo clocks (CQ and CQ) that are delivered
simultaneously with data.
• +1.8V core power supply and 1.5, 1.8V VDDQ,
used with 0.75, 0.9V VREF.
• HSTL input and output levels.
• Registered addresses, write and read controls,
byte writes, data in, and data outputs.
• Full data coherency.
• Boundary scan using limited set of JTAG 1149.1
functions.
• Byte write capability.
• Fine ball grid array (FBGA) package
- 15mm x 17mm body size
- 1mm pitch
- 165-ball (11 x 15) array
• Programmable impedance output drivers via 5x
user-supplied precision resistor.
Description
The 72Mb IS61DDB22M36 and
IS61DDB24M18 are synchronous, high-perfor-
mance CMOS static random access memory
(SRAM) devices. These SRAMs have a common I/O
bus. The rising edge of K clock initiates the
read/write operation, and all internal operations are
self-timed.
Refer to the Timing Reference Diagram for Truth
Table on page 8 for a description of the basic opera-
tions of these DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO SRAMs.
The input addresses are registered on all rising
edges of the K clock. The DQ bus operates at
double data rate for reads and writes. The following
are registered internally on the rising edge of the K
clock:
• Read and write addresses
• Address load
• Read/write enable
Byte writes
• Data-in
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc.
Rev. B
11/10/09
The following are registered on the rising edge of
the K clock:
• Byte writes
• Data-in for second burst addresses
Byte writes can change with the corresponding data-
in to enable or disable writes on a per-byte basis. An
internal write buffer enables the data-ins to be regis-
tered one cycle later than the write address. The first
data-in burst is clocked with the rising edge of the
next K clock, and the second burst is timed to the
following rising edge of the K clock.
During the burst read operation, at the first burst the
data-outs are updated from output registers off the
second rising edge of the C clock (1.5 cycles later).
At the second burst, the data-outs are updated with
the third rising edge of the corresponding C clock
(see page 9). The K and K clocks are used to time
the data-outs whenever the C and C clocks are tied
high.
The device is operated with a single +1.8V power
supply and is compatible with HSTL I/O interfaces.
1
1 page 
72 Mb (2M x 36 & 4M x 18)
DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO Synchronous SRAMs
D
I3
The data-in provided for writing is initially kept in write buffers. The information on these buffers is written into
the array on the following write cycle. A read cycle to the last write address produces data from the write
buffers. Similarly, a read address followed by the same write address produces the latest write data. The
SRAM maintains data coherency.
During a write, the byte writes independently control which byte of any of the two burst addresses is written
(see X18/X36 Write Truth Tables on page 9 and Timing Reference Diagram for Truth Table on page 8).
Whenever a write is disabled (R/W is high at the rising edge of K), data is not written into the memory.
RQ Programmable Impedance
An external resistor, RQ, must be connected between the ZQ pin on the SRAM and VSS to enable the SRAM
to adjust its output driver impedance. The value of RQ must be 5x the value of the intended line impedance
driven by the SRAM. For example, an RQ of 250Ω results in a driver impedance of 50Ω. The allowable range
of RQ to guarantee impedance matching is between 175Ω and 350Ω, with the tolerance described in
Programmable Impedance Output Driver DC Electrical Characteristics on page 13. The RQ resistor should
be placed less than two inches away from the ZQ ball on the SRAM module. The capacitance of the loaded
ZQ trace must be less than 3 pF.
The ZQ pin can also be directly connected to VDDQ to obtain a minimum impedance setting. ZQ must never
be connected to VSS.
Programmable Impedance and Power-Up Requirements
Periodic readjustment of the output driver impedance is necessary as the impedance is greatly affected by
drifts in supply voltage and temperature. At power-up, the driver impedance is in the middle of allowable
impedances values. The final impedance value is achieved within 1024 clock cycles.
Single Clock Mode
This device can be also operated in single-clock mode. In this case, C and C are both connected high at
power-up and must never change. Under this condition, K and K will control the output timings.
Either clock pair must have both polarities switching and must never connect to VREF, as they are not differ-
ential clocks
Depth Expansion
The following figure depicts an implementation of four 4M x 18 DDR-II SRAMs with common I/Os. In this appli-
cation example, the second pair of C and C clocks is delayed such that the return data meets the data setup
and hold times at the memory controller.
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc.
Rev.
11/10/09
5
5 Page 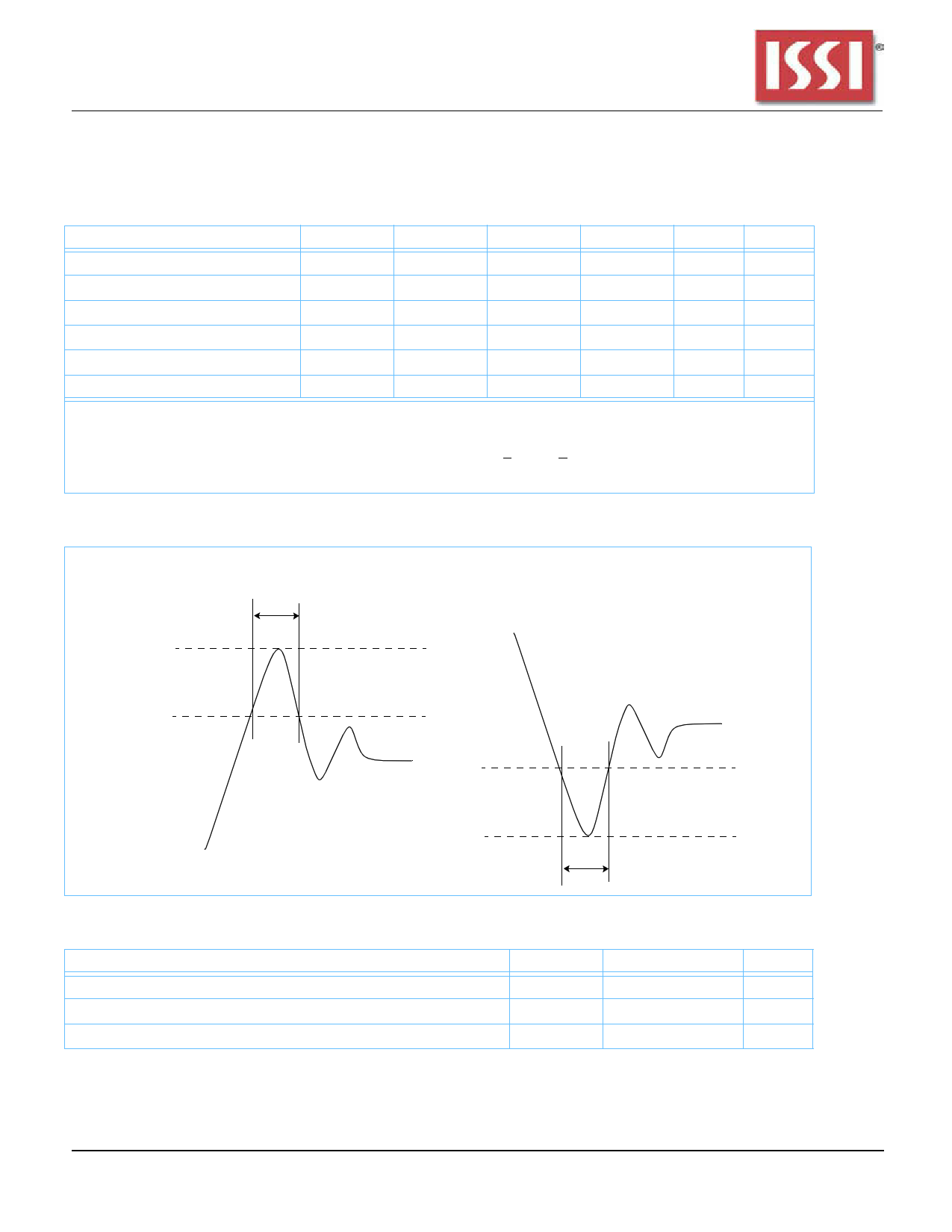
72 Mb (2M x 36 & 4M x 18)
DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO Synchronous SRAMs
Recommended DC Operating Conditions (TA = 0 to +70° C)
Parameter
Symbol
Minimum
Typical
Supply voltage
Output driver supply voltage
Input high voltage
Input low voltage
Input reference voltage
Clocks signal voltage
VDD
VDDQ
VIH
VIL
VREF
VIN - CLK
1.8 - 5%
1.4
VREF +0.1
-0.3
0.68
-0.3
1. All voltages are referenced to VSS. All VDD, VDDQ, and VSS pins must be connected.
2. VIH(Max) AC = See 0vershoot and Undershoot Timings.
3. VIL(Min) AC = See 0vershoot and Undershoot Timings.
4. VIN-CLK specifies the maximum allowable DC excursions of each clock (K, K, C, and C).
5. Peak-to-peak AC component superimposed on VREF may not exceed 5% of VREF.
Maximum
1.8 + 5%
1.9
VDDQ + 0.3
VREF - 0.1
0.95
VDDQ + 0.3
0vershoot and Undershoot Timings
Units
V
V
V
V
V
V
Notes
1
1
1, 2
1, 3
1, 5
1, 4
20% Min Cycle Time
VDDQ+0.6V
VIL(Min) AC
Undershoot Timing
VDDQ
VIH(Max) AC
Overshoot Timing
GND
GND-0.6V
20% Min Cycle Time
PBGA Thermal Characteristics
Item
Thermal resistance junction to ambient (airflow = 1m/s)
Thermal resistance junction to case
Thermal resistance junction to pins
Symbol
RΘJA
RΘJC
RΘJB
Rating
18.6
4.3
1.77
Units
° C/W
° C/W
° C/W
Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc.
Rev. B
11/10/09
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 25 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet IS61DDB24M18.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| IS61DDB24M18 | DDR-II (Burst of 2) CIO Synchronous SRAMs | Integrated Silicon Solution |
| IS61DDB24M18A | 72Mb DDR-II (Burst 2) CIO SYNCHRONOUS SRAM | Integrated Silicon Solution |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
